Long-term lack of movement will reduce the organ function of the organ by 30%, increasing the risk of multiple chronic diseases. The more suffocating news than this is: An European study shows that as long as you stop exercising for more than ten da...

Long-term lack of movement will reduce the organ function of the organ by 30%, increasing the risk of multiple chronic diseases.
The more suffocating news than this is: An European study shows that as long as you stop exercising for more than ten days, your body begins to change.
Life Times combines foreign research and visits experts to tell you what changes will happen to the human body when you move.
Two-week no-motion, cardiovascular degradationA new study released at the European Association for Research on Diabetes (EASD) annual meeting found that even short-term mishealth and sedentary life can affect physical health.
This study included a group of people who could walk more than 10,000 steps a day, 18 women and 10 men. The average age is 32 years old, and the average weight index (BMI) is 24.3kg/m².
Compared with each individual's baseline activity, the study participants reduced the average daily rate by about 10,000 steps, and increased the average daily time of sitting by 103 minutes.
14 days later, cardiovascular function in these people decreased by 1.8%. But after 14 days of normal activity, the function returned to the baseline level.
The researchers also found that the reduction in exercise volume over 2 weeks also led to a decrease in cardiopulmonary function, increased waistline, liver fat deposition and insulin resistance, and a significant decrease in endothelial function, but these indicators could all be restored to baseline levels after the activity volume was restored.
3 minutes of exercise can have health benefitsFor people who are not active or even suffering from cardiovascular disease, will it be too late to start exercising?
A study at the University of British Theatre Bridge answered this question:
No matter what kind of movement was before, starting exercise may reduce all-cause mortality now.
The researchers analyzed the age, height, weight, diet, medical history and other information of 14,000 participants, evaluated their sports status over a period of time through questionnaires and joint monitoring of exercise heart rate, and conducted 4 visits.
Results show that
The death risk for people with medium and high movements is 28% and 33% lower than those with almost non-motivating low movements.
When their movement volume increased to 10 kJ/kg/day and 14.4 kJ/kg/day, the death risk decreased to 38% and 42% respectively.
Increased movement to 6.4 kJ/kg/day by 24% of people who are almost unmoving can also reduce death risk by 24%.

The World Health Organization pointed out that insufficient sports has become the fourth largest risk factor affecting global mortality rates.
Effects can strengthen the heart, strengthen the brain, reduce mortality, and bring many benefits to the body.
1 Promote muscle and bone growth
Exercise can strengthen muscle strength and improve internal muscle fat ratio.
Muscles attach to the bones, and muscle contraction can stimulate increased bone mass. Exercise more outdoor exercises can increase bone elasticity and impotence and prolong the relaxed development of bone quality.
2 Improve cardiopulmonary function
Long-term regular exercise can increase the weight and volume of the heart, increase the heart rate when calm, and thicken the ventricular wall of the myocardium, which will make each contraction stronger and stronger.
3 Preventing and treating cardiovascular and brain vascular diseases
movement can help enhance blood vessel elasticity, control blood pressure, prevent or relieve atherosclerosis, etc.
4 Better sleep
Exercise can prolong sleep duration and improve sleep quality.
5 Relieve emotions and reduce pressure. Exercise can promote the synthesis of serotonin and dopamine in the body. These are the chemical substances in the brain that determine happiness and can effectively relieve people's anxiety.
Effect can also reduce the content of corticoalcohol, help improve memory and focus, and make work more efficient.
There are many "pyramid" for scientific sports. There are many benefits to sports, but excessive and insufficient are just as unhealthy. Scientific, safe and effective training are the key, and it is recommended to follow the "Scientific Fitness Pyramid" for reasonable training.
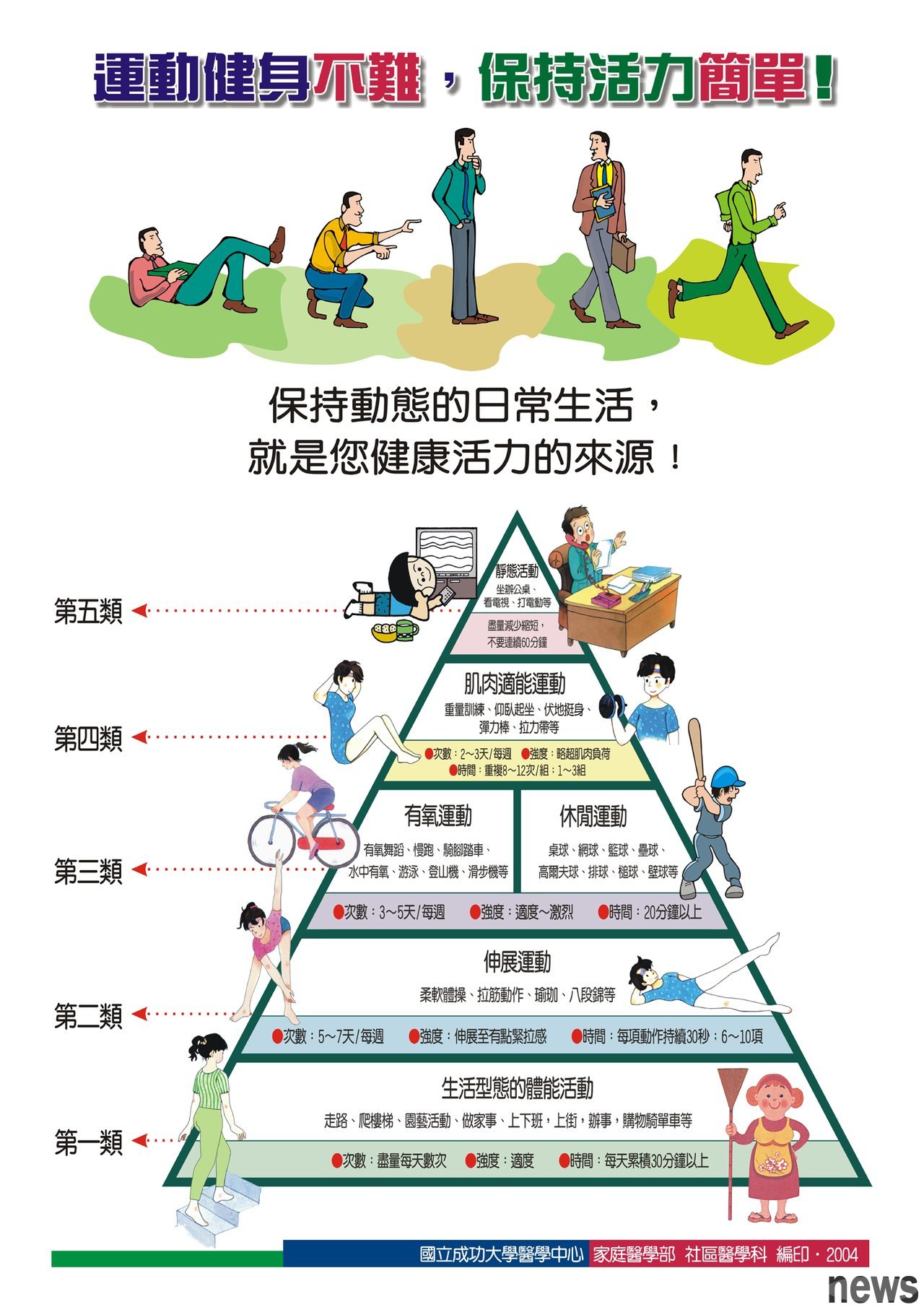
The "Scientific Fitness Pyramid" divides sports behavior into five categories according to at least frequency:
Life-type physical activities include climbing stairs, doing housework, shopping, walking dogs, etc. It is recommended that the event last more than 30 minutes and can be held every day.
Stretching movement
includes soft masturbation, stretching movements, etc. It is recommended that each action lasts 30 seconds per time, 6 to 10 actions as a set, and can be performed for 3 to 7 days a week.
Aerobic + leisure sports
include swimming, mountaineering, billiards, badminton, netball, etc. Do these activities for more than 20 minutes each time, and take them for 3 to 5 days a week.
Muscles are suitable for exercise, including semi-squats, squats, sitting up, push-ups, etc. 8~12 times are one set, do 1~3 sets at a time, and do 2~3 days a week.
Static activities
include sitting in the office, watching TV, playing games, etc. It is necessary to reduce or shorten the time of this type of activity as much as possible. It is best not to continue for 60 minutes or more.
This article is redirected from Lifetime News WeChat (ID: LT0385)